Overview
こんにちは pon です。
全文検索エンジンは男の夢です。故に全文検索ライブラリであるLuceneの内部を理解するためにIndexWriterの実装をコードで追います。IndexWriterを追うことで内部のインデックスのデータ構造などを学べるはずです。まずは第一弾として 「DWPT, IndexingChain 導入編」 を書きました。
Luceneに触れるのが初めての人は私の過去ブログがおすすめです。 Elasticsearchを理解するためにLuceneを使った検索エンジン構築に入門してみた
IndexWriter
IndexWriterは前回のブログで説明したように下記のアーキテクチャを持ちます。
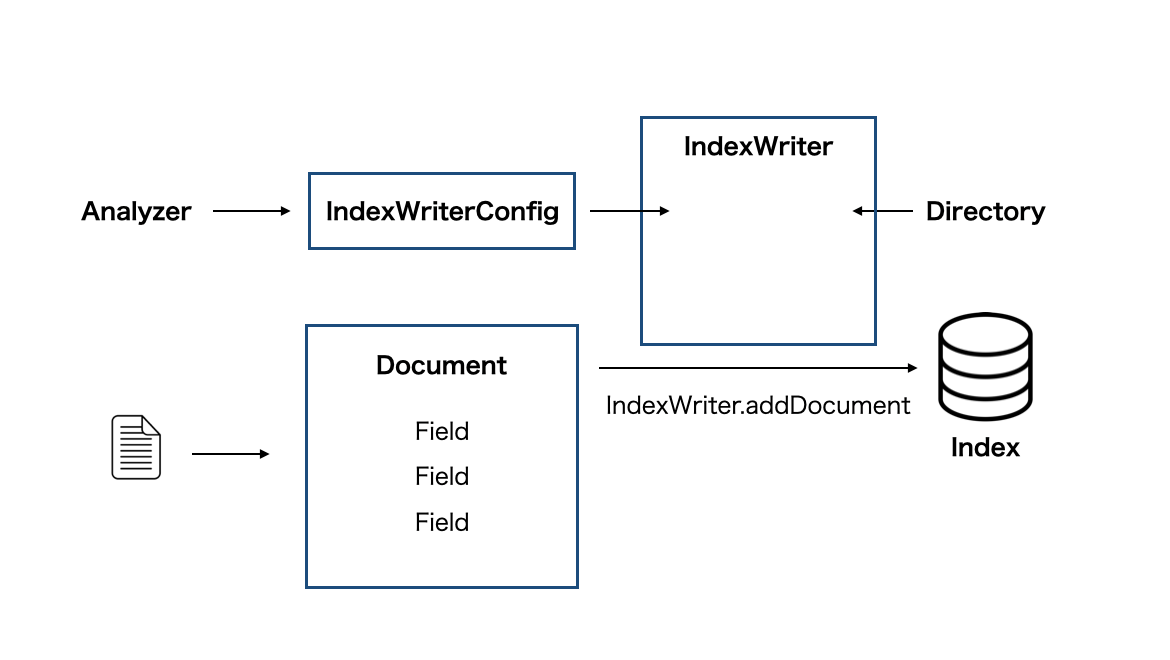
IndexWriterのメインの処理であるドキュメント追加処理IndexWriter.addDocumentから追っていきましょう。
public long addDocument(Iterable<? extends IndexableField> doc) throws IOException {
return updateDocument(null, doc);
}
内部を見るとupdateDocumentが呼ばれています。実はaddはupdateのwrap関数だったのです。実際に updateDocumentをみてみましょう。
public long updateDocument(Term term, Iterable<? extends IndexableField> doc) throws IOException {
return updateDocuments(term == null ? null : DocumentsWriterDeleteQueue.newNode(term), List.of(doc));
}
なにやらDocumentsWriterDeleteQueueというクラスがなにやらNodeを追加しています。実はLuceneのupdate処理はdeleteした後にaddしているのです。これはドキュメントにも記載があります。
Updates a document by first deleting the document(s) containing term and then adding the new document. The delete and then add are atomic as seen by a reader on the same index (flush may happen only after the add).
つまりupdateはdeleteしてからaddする処理であり、この処理はアトミックです。DocumentsWriterDeleteQueueが必要となるのはdocumentのupdate処理のときだけであり、addDocumentから呼ばれた時は削除対象のドキュメント識別termがnullで渡されるため、DocumentsWriterDeleteQueueは不要になります。ドキュメント識別termは例えばid指定でupdateしたい場合は下記のように呼び出します。
writer.updateDocument(new Term("id", "001"), doc2);
DocumentsWriterDeleteQueueという名前から削除に関してはQueueを使って実装されていることがわかります。
続いてupdateDocumentsをみていきます。
private long updateDocuments(final DocumentsWriterDeleteQueue.Node<?> delNode, Iterable<? extends Iterable<? extends IndexableField>> docs) throws IOException {
ensureOpen();
boolean success = false;
try {
final long seqNo = maybeProcessEvents(docWriter.updateDocuments(docs, delNode));
success = true;
return seqNo;
} catch (VirtualMachineError tragedy) {
// ...
} finally {
// ...
}
}
DocumentsWriter クラスであるdocWriterがupdate処理を引き受けます。
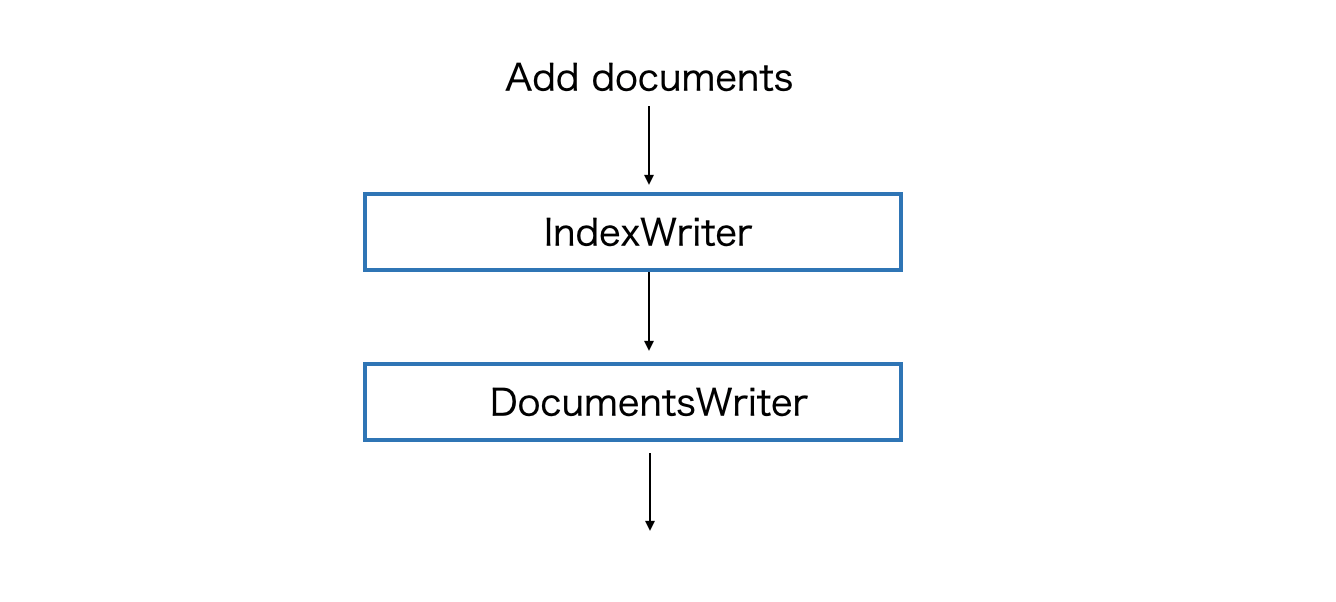
long updateDocuments(final Iterable<? extends Iterable<? extends IndexableField>> docs,
final DocumentsWriterDeleteQueue.Node<?> delNode) throws IOException {
boolean hasEvents = preUpdate();
final DocumentsWriterPerThread dwpt = flushControl.obtainAndLock();
final DocumentsWriterPerThread flushingDWPT;
long seqNo;
try {
// This must happen after we've pulled the DWPT because IW.close
// waits for all DWPT to be released:
ensureOpen();
final int dwptNumDocs = dwpt.getNumDocsInRAM();
try {
seqNo = dwpt.updateDocuments(docs, delNode, flushNotifications);
} finally {
if (dwpt.isAborted()) {
flushControl.doOnAbort(dwpt);
}
numDocsInRAM.addAndGet(dwpt.getNumDocsInRAM() - dwptNumDocs);
}
final boolean isUpdate = delNode != null && delNode.isDelete();
flushingDWPT = flushControl.doAfterDocument(dwpt, isUpdate);
} finally {
// ...
}
// ...
}
ここでDWPTという概念が登場します。これは DocumentsWriterPerThread の略でLuceneのコードやドキュメントで度々この単語が登場します。複数のスレッドにドキュメント更新を分散させます。各DWPTが個別にメモリを管理しており、ドキュメント追加でメモリに十分なドキュメントを保持すると、DWPTはフラッシュ処理ですべての変更をディレクトリに永続化します。
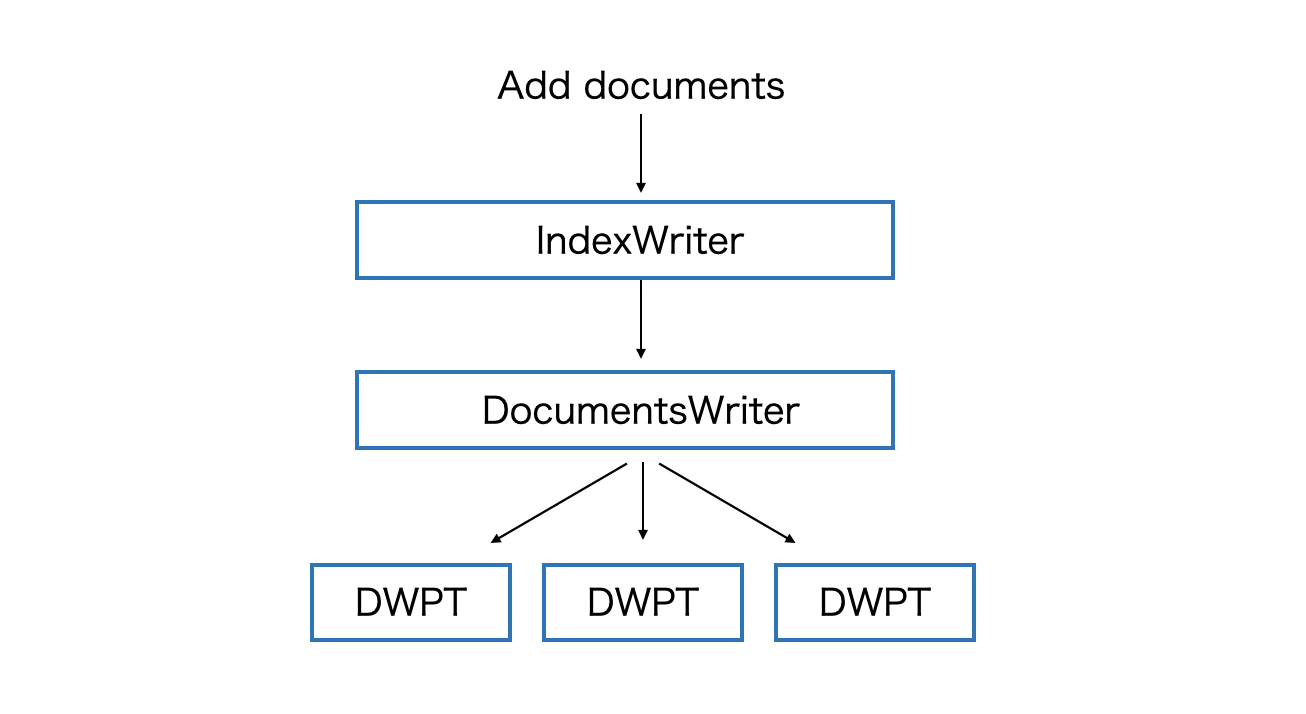
各DWPTは、書き込まれる1つのセグメントに対応します。各DWPTが独立した場所でtokenizeなどを行います、tokenizeなどの処理にはロックが不要ですがFlush時にはLockを必要とします。
DWPTの概要を掴んだところでDocumentsWriterPerThread.updateDocumentsを覗いていきましょう。
long updateDocuments(Iterable<? extends Iterable<? extends IndexableField>> docs, DocumentsWriterDeleteQueue.Node<?> deleteNode, DocumentsWriter.FlushNotifications flushNotifications) throws IOException {
try {
testPoint("DocumentsWriterPerThread addDocuments start");
assert abortingException == null: "DWPT has hit aborting exception but is still indexing";
if (INFO_VERBOSE && infoStream.isEnabled("DWPT")) {
infoStream.message("DWPT", Thread.currentThread().getName() + " update delTerm=" + deleteNode + " docID=" + numDocsInRAM + " seg=" + segmentInfo.name);
}
final int docsInRamBefore = numDocsInRAM;
boolean allDocsIndexed = false;
try {
for (Iterable<? extends IndexableField> doc : docs) {
reserveOneDoc();
indexingChain.processDocument(numDocsInRAM++, doc);
}
allDocsIndexed = true;
return finishDocuments(deleteNode, docsInRamBefore);
} finally {
if (!allDocsIndexed && !aborted) {
// the iterator threw an exception that is not aborting
// go and mark all docs from this block as deleted
deleteLastDocs(numDocsInRAM - docsInRamBefore);
}
}
} finally {
maybeAbort("updateDocuments", flushNotifications);
}
}
ここで重要なのは indexingChain です。このクラスは存在する全てのフィールドの型に応じて処理していきます。実際にフィールドごとに processFieldを呼んでいます。
void processDocument(int docID, Iterable<? extends IndexableField> document) throws IOException {
// ...
try {
for (IndexableField field : document) {
fieldCount = processField(docID, field, fieldGen, fieldCount);
}
} finally {
// ...
}
// ...
}
ではprocessFieldをみていきます。
private int processField(int docID, IndexableField field, long fieldGen, int fieldCount) throws IOException {
// ...
// Invert indexed fields:
if (fieldType.indexOptions() != IndexOptions.NONE) {
// ...
}
// Add stored fields:
if (fieldType.stored()) {
// ...
}
if (dvType != DocValuesType.NONE) {
// ...
}
if (fieldType.pointDimensionCount() != 0) {
// ...
}
return fieldCount;
}
Indexing Chain内では、フィールドのタイプごとに下記の順番でフィールドが処理されていきます。
- inverted index
- store
- doc_values
- point
storeやdoc_valuesはElasticsearchに精通していればすぐにピンとくるはずです。説明はElasticsearchのドキュメントに任せます。
store Elasticsearch store
doc_values Elasticsearch doc_values
ポイントバリューは数値を表し、通常のテキストとは異なるインデックスが付けられます。転置インデックスの代わりに、ポイントはKDツリーなどのデータ構造でインデックス付けされます。
まとめ
IndexWriterのaddがupdateのwrapであること、deleteはQueueで実装されていることを確認し、DWPT、IndexingChainなどの概念を簡単に抑えました。
次回から更にフィールド毎の処理やアルゴリズムを追っていきます。